
Research Overview
As part of the National Key Research and Development Programme, the Institute of Geophysics of the China Earthquake Administration (IGU) initiated a detailed study of the Freshwater River-Longmenshan-Anning River-Daliangshan Fracture Zone in mid-September 2020. The project aims to analyze:
- Microseismic Activity: Understanding the frequency and distribution of small-scale earthquakes.
- Fault Morphology: Mapping the physical structure and dynamics of the fault zones.
- Deep Structural Characteristics: Investigating the underlying geological features that influence tectonic activity.
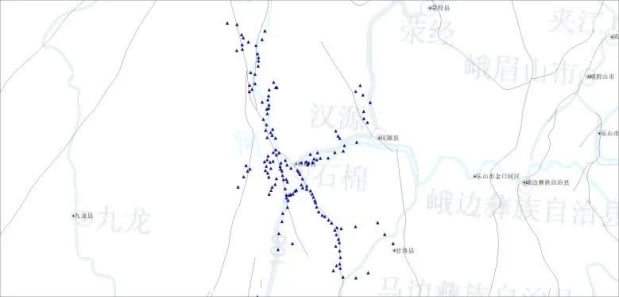
Special Focus: The “Three Forks” Area
Located at the intersection of the Freshwater River, Longmenshan, and Anning River fault zones, the “Three Forks” area is a unique tectonic region on the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Known for its high seismicity, this area serves as a natural laboratory for studying:
- The seismic behavior of the Sichuan-Yunnan rhomboid-shaped block.
- The deep deformation and morphology of one of the most seismically active regions on the planet.
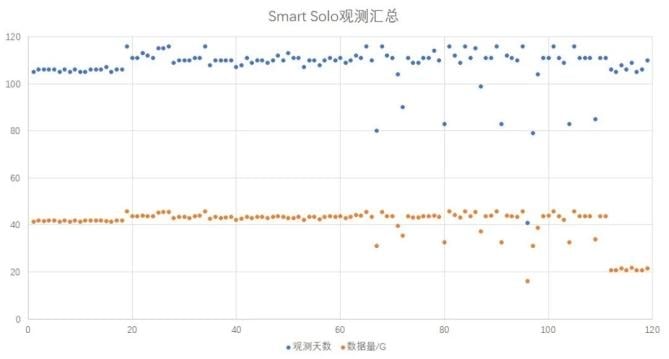
Equipment Deployed
The project utilized 160 units of the SmartSolo IGU-16HR EB 3C short-cycle, integrated seismic observation system. This advanced equipment provided significant advantages:
- Compact and Lightweight: Facilitating easy transport and deployment.
- Simple Operation: Streamlined setup for efficient fieldwork.
- Durability: Exceptional waterproofing and endurance capabilities.
- Extended Power Supply: Supporting continuous data collection for up to 130 days.
Observation Timeline
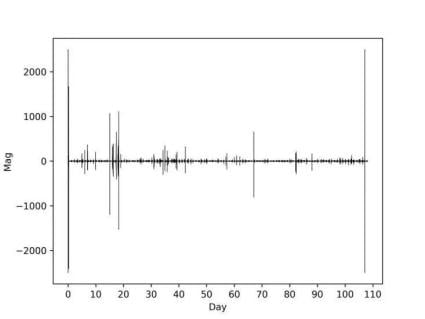
- Duration: 105 days (mid-September 2020 to early January 2021).
- Data Collected: Approximately 5TB of high-quality raw seismic data.
- Power Reserve: Devices retained sufficient power for an additional 25 days of operation.
Significance of the Study
This project offers critical insights into:
- Seismicity Patterns: Identifying areas of heightened microseismic activity.
- Fault Zone Dynamics: Providing detailed information on fault morphology and movement.
- Tectonic Processes: Enhancing our understanding of the deformation characteristics of the Tibetan Plateau’s eastern margin.
The findings are expected to contribute significantly to:
- Earthquake risk assessment in the Sichuan-Yunnan region.
- Improved disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Advancing geophysical research methodologies for tectonic studies.
Conclusion
The Tectonic Regional Study of the Fracture Zone on the Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau underscores the importance of cutting-edge seismic monitoring technologies like SmartSolo IGU-16HR EB 3C. By enabling precise and efficient data collection in challenging environments, this project paves the way for a deeper understanding of earthquake mechanisms and tectonic processes, fostering safer and more resilient communities in seismic-prone regions.
