Overview of the Arthur River Earthquake
On 5 January 2022, residents of Western Australia’s Southern Wheatbelt experienced a 4.0 magnitude earthquake. The event caused visible damage, such as cracks in stone masonry and fallen objects, surprising many despite the region’s location in the South West Seismic Zone, one of Australia’s most active seismic areas.
Rapid Deployment with SmartSolo Technology
Western Australia previously lacked a rapid deployment capability for earthquake monitoring. This changed with Dr. Huaiyu Yuan of Macquarie University, in collaboration with the Centre for Exploration and Positioning at the University of Western Australia, acquiring SmartSolo IGU-BD3c-5 seismometers. The Arthur River earthquake provided an opportunity to test these advanced instruments in collaboration with the Department of Fire and Emergency Services (DFES) and the Geological Survey of Western Australia (GSWA).
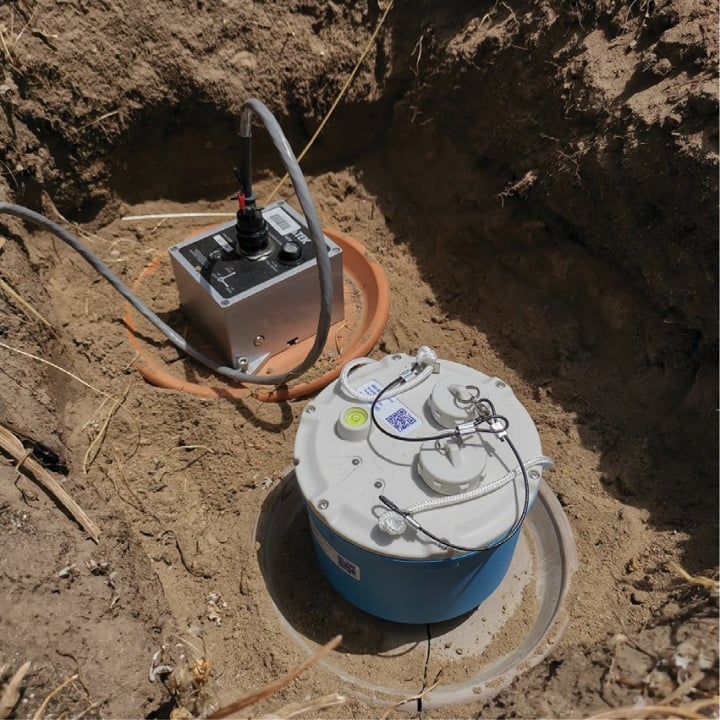

Deployment and Data Collection
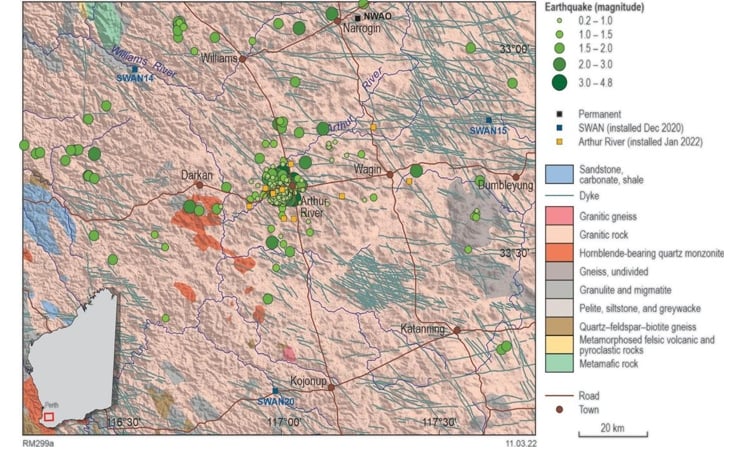
- Initial Deployment: On 10 January 2022, six additional seismic instruments were installed near Arthur River, enhancing the SWAN network.
- Community Collaboration: DFES used regional networks to engage the community, ensuring efficient deployment of equipment.
- Additional Support: Retired seismologists from the Seismologists’ Association of Australia also contributed an instrument to the effort.
Key Findings
Seismic Events Analysis
During the first three weeks of deployment:
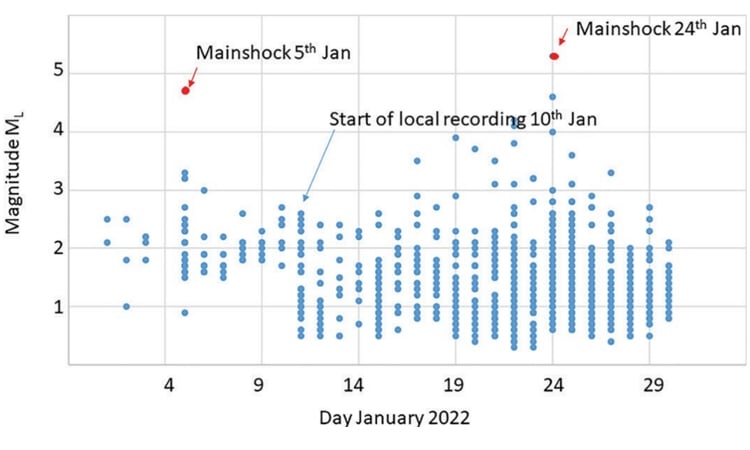
- Geoscience Australia Data: 94 events were initially recorded using ANSN.
- Local Monitoring Results: Over 950 earthquakes were identified, concentrated in clusters west of Arthur River, with magnitudes as low as -0.3.
Improved Monitoring with SmartSolo
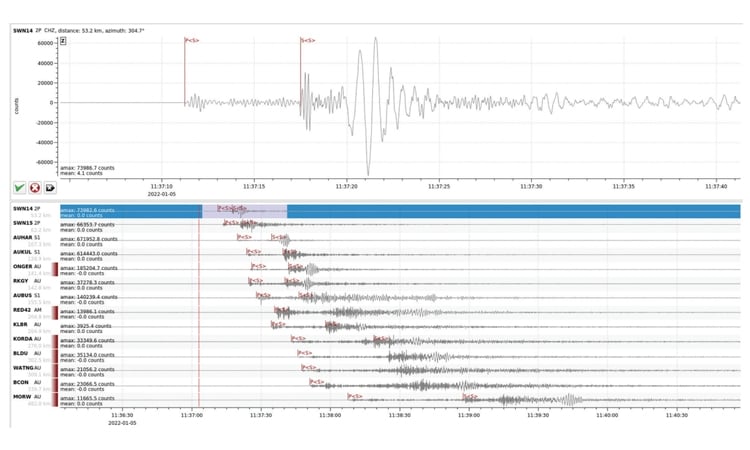
- The SmartSolo seismometers provided precise P- and S-wave picks using machine learning algorithms.
- Localized monitoring significantly increased event detection, particularly for low-magnitude earthquakes.
Contribution to Seismic Hazard Understanding
The data from the Arthur River swarm will:
- Enhance Understanding of Ground Motion:
- Strong motion data will inform the effects of earthquakes on infrastructure in southwest Western Australia.
- Guide National Seismic Hazard Assessment:
- The results will support updates to hazard models, like the National Seismic Hazard Assessment.
- Increase Community Awareness:
- Findings will be used by DFES and Geoscience Australia to educate residents on earthquake risks and preparedness.
Conclusion
The successful rapid deployment of SmartSolo seismometers for the Arthur River earthquake demonstrates the potential for advanced seismic monitoring to transform our understanding of earthquake hazards. This effort not only enhances regional earthquake monitoring capabilities but also provides critical insights to guide infrastructure resilience and community safety in seismic zones.