
Introduction to Antarctic Geophysical Investigations
Understanding the tectonic history of Antarctica requires comprehensive geophysical investigations. Techniques such as geomagnetic, seismic, and aeromagnetic gravimagnetic studies are essential for probing the subsurface. However, traditional methods often lack the resolution needed to reveal detailed structures beneath the ice sheet.
Ice-penetrating radar offers high-resolution reflectivity images of the ice sheet, but it does not provide critical insights into the physical properties of sub-ice geological formations. To overcome these limitations, scientists have deployed advanced seismic technologies to gain deeper insights into the geology of East Antarctica.
Study Overview: The Rathman Hills, Prydz Bay
Objectives and Challenges
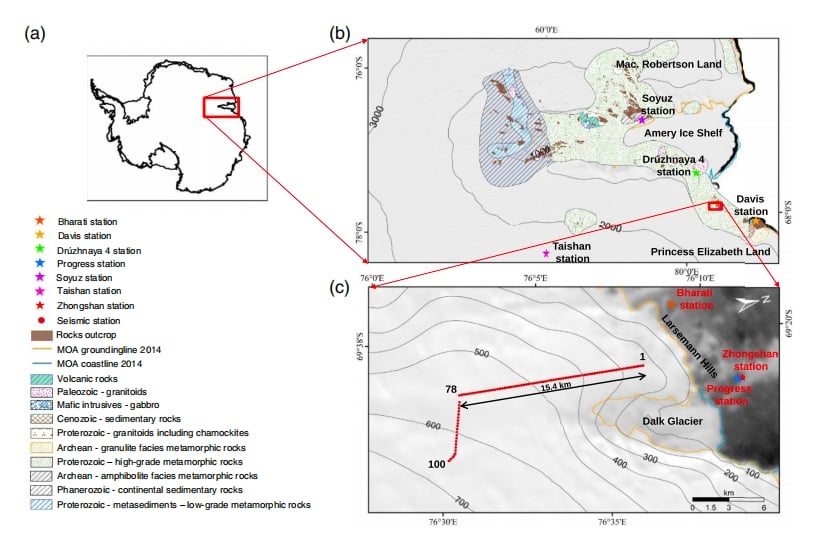
The primary goal of this study was to obtain high-resolution images of the ice sheet and uppermost crustal structure beneath Mount Rathman in Prydz Bay, East Antarctica. This region’s subglacial environment is complex, and understanding its geological evolution requires innovative methods.
Equipment and Configuration
To achieve this, researchers used an ambient noise seismic experiment, deploying 100 SmartSolo IGU-BD3C-5 short-period seismometers. These units were spaced at 200-meter intervals, forming a dense linear desk array capable of capturing detailed seismic data.
The SmartSolo seismometers are highly sensitive instruments designed for challenging environments. Their ability to operate effectively in extreme conditions makes them ideal for Antarctic research.
Key Findings and Insights
Subglacial Intrusive Rock Discovery
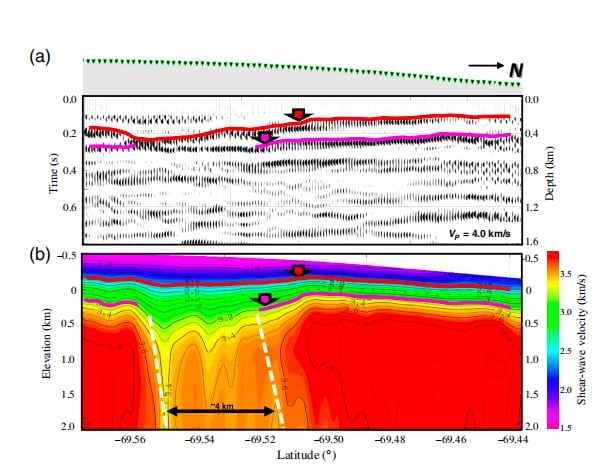
Preliminary results from this groundbreaking study suggest the presence of a near-vertical, ice-sheet-covered intrusive rock formation. This structure spans a horizontal extent of up to 4 kilometers. Such discoveries are critical for understanding the tectonic and geological processes shaping the Antarctic continent.
Advancements in Subglacial Imaging
This study highlights the capability of dense linear desk array imaging to:
- Capture high-resolution seismic images of ice and crustal structures.
- Provide insights into subglacial geological formations.
- Enhance understanding of physical properties beneath the ice sheet.
Implications for Antarctic Research
The results from the Rathman Hills study contribute significantly to our understanding of the subglacial environment in Prydz Bay. These findings will:
- Advance knowledge of Antarctic tectonics and crustal evolution.
- Support future geophysical studies in polar regions.
- Inform models of the Antarctic’s geological history and its role in global tectonic processes.
Conclusion
Dense linear desk array imaging using SmartSolo seismometers has proven to be a powerful tool for Antarctic exploration. By revealing detailed subglacial structures and advancing our geological knowledge, this research sets the stage for future investigations into the ice-covered regions of our planet.
